Insights of Binary Search
The size of search spaces ([l, m] or [m, l]) is reduced roughly by a half of the previous iteration, and will eventually reduced to 2 elements and then 1 element at last.
Priciples of Binary Search
- we must guarantee the search space will decrease over timr (after each iteration).
- we must guarantee the target will not be ruled out when the value of left or right index changes. (it is critical to define how to move the range for searching)
Classical Binary Search
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
|
public int binarySearch(int[] arr) {
int left = 0;
int right = arr.length - 1;
while (left <= right) { // why there include =, if arr size is 1, like target = 4, arr {4}....
int mid = left + (right - left) / 2;
if (arr[mid] == target) {
return mid;
} else if (arr[mid] < target) {
left = mid + 1; // left = mid; wrong! the dead loop will happen when search space <= 2
} lese {
right = mid - 1;
}
}
return -1;
}
|
Time Complexity: O(log_2(n))
… in 2D Space
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
|
public boolean isFind(int[][] matrix, int target) {
if (matrix.length == 0 || matrix[0].length == 0) {
return false;
}
int r = matrix.length;
int c = matrix[0].length;
int left = 0;
int right = r * c - 1;
while (left <= right) {
int mid = left + (right - left) / 2;
int row = mid / r;
int col = mid % c;
if (matrix[row][col] == target) {
return true;
} else if (matrix[row[row][col] < target) {
left = mid + 1;
} else {
right = mid - 1;
}
return false;
}
}
|
Time Complexity: O(log_2(m*n))
Closest Element to Target
when you only have 2 elements in the search space, then you only need to check whether the left or right is the answer.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
|
public int binarySearch(int[] arr, int target) {
int left = 0;
int right = arr.length - 1;
while (left < right - 1) { // when left neighbors right, we terminate the loop
int mid = left + (right - left) / 2;
if (arr[mid] == target) {
return mid;
} else if (arr[mid] < target) {
left = mid;
} else {
right = mid;
}
}
if (Math.abs(arr[left] - target) < Math.abs(arr[right] - target)) {
return left;
} else {
return right;
}
}
|
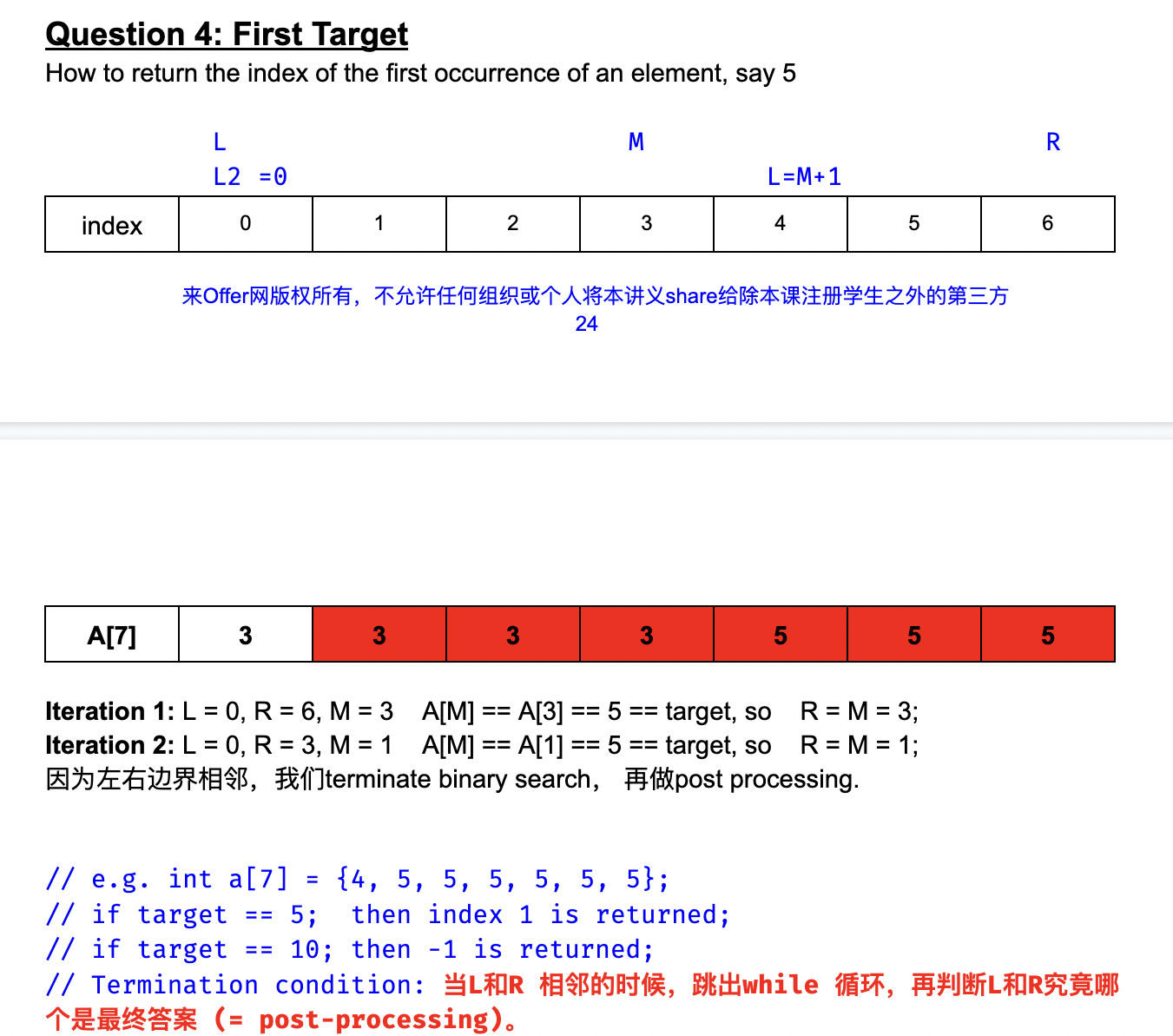
First Target
return the first occurrence of the index.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
|
public int binarySearch(int[] arr, int target) {
int left = 0;
int right = arr.length - 1;
while (right < left - 1) {
int mid = left + (right - left) / 2;
if (arr[mid] >= target) {
right = mid;
} else {
left = mid;
}
}
if (arr[left] == target) {
return left;
} else if (arr[right] == target) {
return right;
} else {
return -1;
}
}
|
Last Target
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
|
public int binarySearch(int[] arr, int target) {
int left = 0;
int right = arr.length - 1;
while (right < left - 1) {
int mid = left + (right - left) / 2;
if (arr[mid] <= target) {
left = mid;
} else {
right = mid;
}
}
if (arr[right] == target) {
return right;
} else if (arr[left] == target) {
return left;
} else {
return -1;
}
}
|
Closest K Elements
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
|
public class Solution {
public int[] kClosest(int[] array, int target, int k) {
// Write your solution here
int left = 0;
int right = array.length - 1;
int[] ans = new int[k];
int i = 0;
if (array.length == 1) {
if (k == 1) {
ans[i] = array[0];
}
return ans;
}
while (left < right - 1) {
int mid = left + (right - left) / 2;
if (array[mid] == target) {
ans[i++] = array[mid];
left = mid - 1;
right = mid + 1;
break;
} else if (array[mid] < target) {
left = mid;
} else {
right = mid;
}
}
for (; i < k; i++) {
if (right >= array.length) {
ans[i] = array[left--];
continue;
}
if (left < 0) {
ans[i] = array[right++];
continue;
}
if (Math.abs(array[left] - target) <= Math.abs(array[right] - target)) {
ans[i] = array[left--];
} else {
ans[i] = array[right++];
}
}
return ans;
}
}
|
Smallest element that is Larger than the target
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
|
public class Solution {
public int smallestElementLargerThanTarget(int[] array, int target) {
// Write your solution here
int left = 0;
int right = array.length - 1;
int i = 0;
if (array == null || array.length == 0) {
return -1;
} else if (array.length == 1) {
if (array[0] > target) {
return 0;
}
return -1;
}
while (left < right - 1) {
int mid = left + (right - left) / 2;
if (array[mid] <= target) {
left = mid;
} else {
right = mid;
}
}
while (left < array.length) {
if (array[left] <= target) {
left ++;
} else {
return left;
}
}
return -1;
}
}
|